Adverbial Clause Of Place - Adverbial Clauses - English Study Here. An adjective or an adverbial clause may express. An adverb clause (or adverbial clause) is a clause that works as an adverb in a sentence. I put it where nobody would find it. All adverbs (including adverbial clauses) can usually be categorized as one of the following Adverbial clauses generally follow the main clause unless otherwise stated.
They are both adverbs of time. Contrast, purpose, cause, effect, comparison, time, place, manner, and condition. Jim miller explains this in more detail in the excerpt from an introduction to english syntax below. (like all clauses, an adverbial clause contains a subject and a verb.) this rule works well with most adverbial clauses (which tend to be adverbs of time, place, or condition). The subjunctive mood is used in adverbial clauses of time and place after the conjunctions whenever and wherever;

Wherever i go i am welcome.
Adverbial clauses introduced by wherever and everywhere are used in a generalizing sense: Its role is to show place, time, condition, degree, and so on. Download pdf adverbial clauses a wide variety of different conjunctions are used to introduce. Keep hitting the gong hourly. An adverbial clause is used as an adverb; He made an impact everywhere that he went. Unlike adverbs, adverbial clauses modify whole clauses rather than just a verb. The subjunctive mood is used in adverbial clauses of time and place after the conjunctions whenever and wherever; He always put things where nobody in their senses would look for them. I put it where nobody would find it. An adverbial clause is a group of words that plays the role of an adverb. This type of clause usually employs. There are many different types:
There are many different types: Wherever i go i am welcome. However, it is not a strict rule. #rils the lingua expert# this video is for those who have confusion with regards to basic and advance english grammar. An adverbial clause of place describes where something has occurred or will occur.
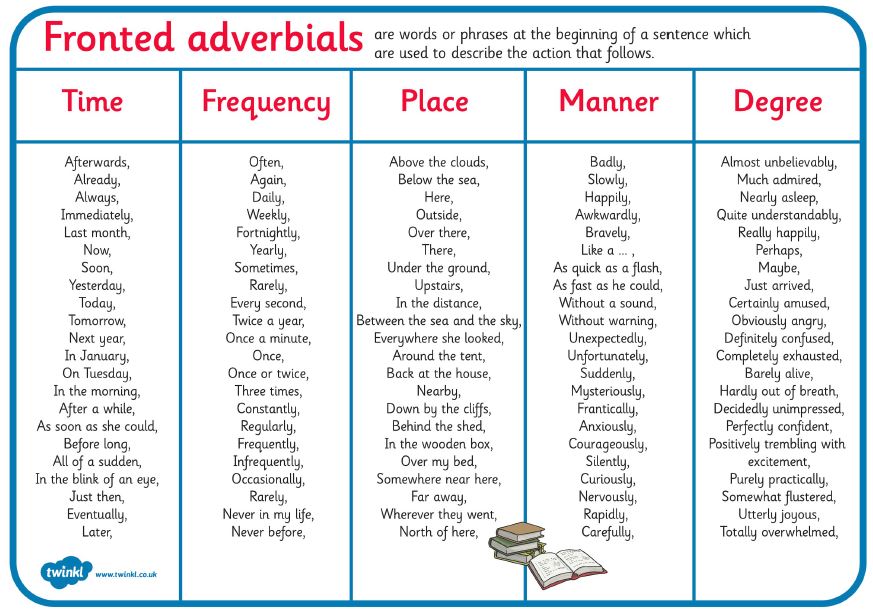
An adverbial clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb.
An adverbial clause may precede the clause to which it is subordinated or follow it. As soon as he received the telegram, he left for his native place. It modifies the main clause and is introduced by subordinating conjunctions such as because, if, when, although, since, etc. As with all clauses, it contains a subject and predicate, though the subject as well as the (predicate) verb may sometimes be omitted and implied. Jim miller explains this in more detail in the excerpt from an introduction to english syntax below. This type of clause usually employs. Wherever i go i am welcome. It means the clause modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adverbial clauses generally follow the main clause unless otherwise stated. He made an impact everywhere that he went. An adverb clause (or adverbial clause) is a clause that works as an adverb in a sentence. Conjunctions used include anywhere, everywhere, where, wherever. #rils the lingua expert# this video is for those who have confusion with regards to basic and advance english grammar.
Clauses of place and time. There are many different types: An adverbial clause is a group of words that plays the role of an adverb. That is, the entire clause modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverbial clause is used as an adverb;

An adverbial clause is a group of words that plays the role of an adverb.
Don't miss our complete guide to adverb clauses with definitions. As soon as he received the telegram, he left for his native place. There are many different types: Like all clauses, an adverb clause has a subject and a predicate. Adverbial clauses generally follow the main clause unless otherwise stated. (like all clauses, an adverbial clause contains a subject and a verb.) this rule works well with most adverbial clauses (which tend to be adverbs of time, place, or condition). He made an impact everywhere that he went. As with all clauses, it contains a subject and predicate, though the subject as well as the (predicate) verb may sometimes be omitted and implied. That is, the entire clause modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. (1) place or time (2) cause (3) concession (4) purpose (5) result (6) condition (7) comparison (8) indirect discourse (9) indirect question. Never walk behind a horse in case it kicks out at you. A place clause is introduced by the subordinators where and wherever. The most common subordinating conjunctions are where adverbial clauses of condition describe the conditions necessary for specific actions or events to happen.

No comments:
Post a Comment